Ramses II, also known as Ramses the Great, remains one of the most legendary figures in ancient Egyptian history. As the third pharaoh of Egypt’s 19th Dynasty, he ruled for an extraordinary 66 years, leaving behind a legacy of military prowess, diplomatic achievements, and architectural wonders that continue to fascinate scholars and historians. His reign marked a golden age for Egypt, characterized by stability, economic growth, and cultural advancements that shaped the civilization’s future.
A Young Prince Destined for Greatness
Born into the royal family, Ramses II was groomed for leadership from an early age. His father, Seti I, a formidable ruler in his own right, ensured that his son received extensive military training and firsthand experience in governance. When Ramses II ascended to the throne in his early twenties, he wasted no time in demonstrating his capability as a leader. He consolidated power swiftly, strengthening Egypt’s position both internally and on the battlefield. His early campaigns and administrative reforms solidified his status as a ruler who was not only divinely appointed but also exceptionally skilled in statecraft.
A Military Genius and Warrior King
Ramses II’s reign was defined in large part by his military campaigns, the most famous of which was the Battle of Kadesh against the Hittite Empire. Taking place around 1274 BCE, this battle is considered one of the largest chariot engagements in history. Facing an enemy with superior numbers, Ramses II’s strategic acumen and sheer determination turned what seemed like an impending defeat into a tactical victory. Though the battle ended in a stalemate, it led to a historic outcome—the signing of the world’s first known peace treaty between the Egyptians and the Hittites. This agreement not only ensured a period of relative stability but also demonstrated Ramses II’s diplomatic skill in securing Egypt’s borders through negotiation as well as warfare.
Beyond Kadesh, Ramses II led successful military expeditions into Nubia, reinforcing Egypt’s dominance over its southern territories. He also extended Egyptian influence into the Levant, ensuring control over key trade routes and fortifying Egypt’s position as the preeminent power in the region. His military exploits not only secured vast amounts of wealth and resources but also cemented his reputation as one of history’s greatest warrior kings.
The Builder Pharaoh: A Legacy in Stone
While Ramses II’s military achievements were remarkable, his contributions to architecture and infrastructure were equally transformative. More than any other pharaoh, he undertook ambitious construction projects designed to glorify his reign and immortalize his name. Among his most breathtaking accomplishments are the temples at Abu Simbel. These colossal rock-cut structures feature four massive statues of Ramses II seated in a commanding posture, a clear display of his divine kingship. The temples served both a religious function and a political one, reinforcing the might of the Egyptian empire to all who entered.
In addition to Abu Simbel, Ramses II played a significant role in expanding and enhancing existing religious complexes, including the grand temples of Karnak and Luxor. He commissioned the Ramesseum, a vast mortuary temple on the west bank of the Nile, adorned with intricate reliefs depicting his military victories, religious devotion, and divine connections. His passion for monumental architecture was not simply a matter of vanity—it was a means of consolidating power, reinforcing religious traditions, and ensuring that his legacy would endure for millennia.
A Pharaoh Worshipped as a Living God
Ramses II understood the power of religious symbolism, and he actively cultivated an image of himself as a god on Earth. Through his grand constructions and extensive self-portrayals in art and inscriptions, he sought to link himself directly to the gods, particularly Amun-Ra, the chief deity of the Egyptian pantheon. His statues and temples depicted him not just as a mortal king but as a divine being worthy of worship. This strategy strengthened his hold on the throne, unifying the people under a ruler who was not only a military and political leader but also a figure of religious significance.
His dedication to the gods also manifested in his restoration of older temples and the commissioning of new religious sites across Egypt. By revitalizing sacred spaces, he ensured the favor of the priesthood while reinforcing the central role of religion in governance. This blending of political power and divine authority allowed Ramses II to maintain stability within the kingdom and project his influence far beyond Egypt’s borders.
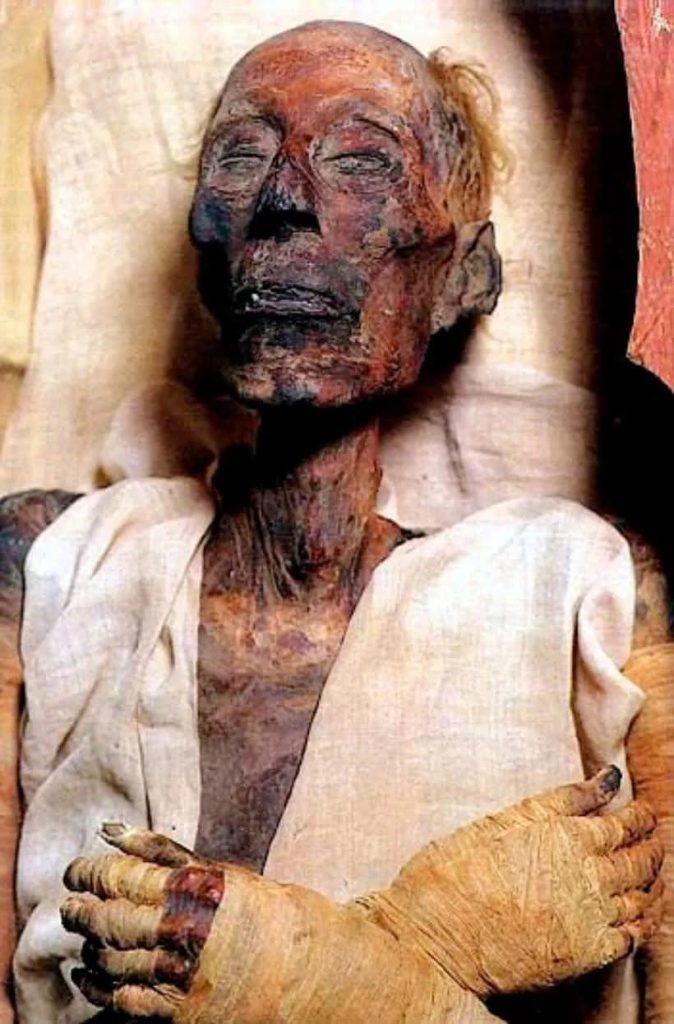
The Discovery of Ramses II’s Mummy: A Glimpse into the Past
For centuries, Ramses II’s legacy was known primarily through his monuments and inscriptions. However, in 1881, an extraordinary archaeological discovery changed our understanding of the great pharaoh—his remarkably well-preserved mummy was found in a secret cache at Deir el-Bahari. Unlike many other royal tombs that had been plundered over the centuries, Ramses II’s remains survived, offering modern scholars invaluable insights into his life, health, and the burial practices of the time.
Scientific analysis of his mummy revealed that he likely suffered from severe arthritis and dental issues in his later years, suggesting that despite his god-like status, he was not immune to the ailments of aging. The discovery of his body reinforced his historical significance, providing tangible evidence of a ruler whose impact on Egypt had endured for over three millennia.
Ramses II’s Enduring Influence
Even today, Ramses II continues to captivate the world. His military conquests, diplomatic ingenuity, and architectural feats make him one of the most studied and celebrated figures in ancient history. His legacy extends beyond Egypt, influencing later civilizations and shaping our understanding of leadership, governance, and empire-building.
In modern times, the colossal statues, intricate temple carvings, and inscriptions bearing his name serve as a testament to his ambition and vision. The grand structures he left behind stand as reminders of Egypt’s power during the New Kingdom and of a ruler who truly earned the title “the Great.” His ability to balance military might with diplomatic acumen, and religious devotion with grand architectural achievements, set a precedent for leadership that few rulers in history have matched.
As we continue to explore and learn from ancient Egypt’s rich history, Ramses II remains a towering figure—one whose reign exemplified the heights of human ambition and the enduring impact of visionary leadership. His life, filled with triumphs and challenges, serves as an enduring example of how one ruler’s vision can shape the destiny of a civilization. Whether through his legendary battles, monumental temples, or the diplomatic breakthroughs that redefined international relations, Ramses II’s influence echoes through the annals of history, solidifying his place among the greatest leaders of all time.





